linear axial compression test on cervical spine|Cervical Orthopedic Tests : agencies This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients with cervical radiculopathy and other upper extremity nerve pathologies. ICF Domain (s): Body structure and function. ICF Categories: . The Stoics elaborated a detailed taxonomy of virtue, dividing virtue into four main types: wisdom, justice, courage, and moderation. Wisdom is subdivided into good sense, good .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webOzyegin University Student Information System
What is the Best Way to Apply the Spurling Test for
the test shale get harder as you continue
Spurling Test: What It Is, Procedure & Positive Results
The Spurling Test is designed to reproduce symptoms by compression of the affected nerve root. The cervical extension is used to induce/reproduce posterior bulging of the . This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients with cervical radiculopathy and other upper extremity nerve pathologies. ICF Domain (s): Body structure and function. ICF Categories: .1. symptom reproduction with cervical compression with the neck in lateral flexion to the side of pain 2. symptom reduction with cervical distraction 3. symptom reproduction with an upper .
After the initial examination, each subject, while seated, underwent six distinct provocative maneuvers of the cervical spine in the following order: lateral bending and axial compression, the original test described by Spurling and . The Spurling test helps a healthcare provider diagnose cervical radiculopathy (a pinched nerve in your neck). You might need this test if you have pain, numbness or muscle . This study aimed to determine an injury criterion and accompanying tolerance values for cervical spine segments in axial compression applied with varying coronal plane .

Cervical disk herniations and degenerative spondylosis are two common conditions that can affect the cervical spine and may lead to neck pain and symptomatic compression of the spinal cord.Several commonly performed provocative tests include Spurling’s Neck Compression Test, Shoulder Abduction (Re-lief) Test, Neck Distraction Test, L’hermitte’s Sign, Hoffmann’s Sign .
the test was really hard
cervical spine C6 nerve root travels under C5 pedicle (mismatch) . foraminal compression test that is specific, but not sensitive, in diagnosing acute radiculopathy . extending the neck, and then applying and axial load . Test for lesions to weight-bearing structures, the facets or for nerve root pathology.Positive if radicular symptoms develop. Negative if symptoms are not pr.After the initial examination, each subject, while seated, underwent six distinct provocative maneuvers of the cervical spine in the following order: lateral bending and axial compression, the original test described by Spurling and . Degenerative cervical spine disease (cervical spondylosis) is osteoarthritis of the spine, which includes the spontaneous degeneration of either disc or facet joints. Presenting symptoms include axial neck pain and neurological complications. The most common neurological complication is cervical spondylotic radiculopathy.

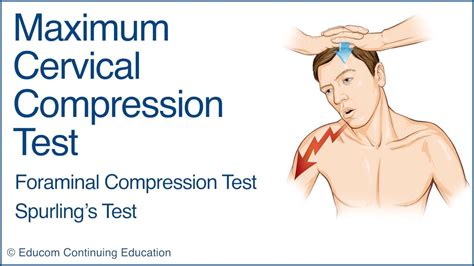
The Maximum Cervical compression test is used to detect nerve root involvement in the cervical spine. This test is also known by other names, including the Foraminal Compression test and Spurling’s test. This test should not be used if a significant cervical injury is suspected. The occurrence of acute myelopathy in a nontrauma setting constitutes a medical emergency for which spinal MRI is frequently ordered as the first step in the patient’s workup. The emergency department radiologist should be familiar with the common differential diagnoses of acute myelopathy and be able to differentiate compressive from noncompressive causes. The .of the spine have involved compression. Perhaps the earliest such study was Messerer 's work on the me-chanical properties of the vertebrae (2). He reported compression breaking loads ranging from 1.47-2.16 kN for the lower cervical spine. Bauze and Ardran loaded human cadaveric cervical spines in compression and re-
The cervical spine is a dynamic structure that protects nervous innervation to the entire body while maintaining the range of motion for the head and neck. It contains seven vertebrae, which provide support to the head while allowing for side flexion, rotation, flexion, and extension.. Cervical spine fractures are a primary cause of mobility loss and mortality in trauma patients, .
The test is positive for cervical radiculopathy if axial loading to the top of the patient's head reproduces the characteristic pain and radicular features. A modification of the Spurling test .
Positive Spurling’s Test (Sign) A positive Spurling’s sign means pain in the shoulder or upper arm on the same side to which the head is tilted.. Positive test (pain after applying pressure) is quite specific for a pinched nerve in the neck (cervical radiculopathy) and greatly reduces the probability of other conditions as a source of pain [1].The test does not .
The bilateral facet joints of the subaxial cervical spine play an important role in load-bearing and kinematics of the neck. They bear over 64% of axial load in the cervical spine 20,22 and are responsible for coupled intervertebral motions in axial rotation and lateral bending. 4,19 The facets also protect the spinal cord by preventing excessive intervertebral axial .
400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA 15096-0001 U.S.A. Tel: (724) 776-4841 Fax: (724) 776-5760 : www.sae.org SAE TECHNICAL PAPER SERIES 2002-22-0022 Tolerance of the Cervical Spine to EccentricThe Axial Cervical Compression test is performed to detect the presence of nerve root involvement in the cervical spine. This test is also known as the cervical compression test. The Axial Cervical Compression test should not be used if . Intramedullary cord hyperintensity at T2-weighted MRI is a common imaging feature of disease in the spinal cord, but it is nonspecific. Radiologists play a valuable role in helping narrow the differential diagnosis by integrating patient history and laboratory test results with key imaging characteristics. The authors present an algorithmic approach to evaluating intrinsic . Cervical Spine Tests That Provide or Relieve Pain Spurling Neck Compression Test . Spurling and Scoville first described the Spurling neck compression test, also known as the foraminal compression test, neck .
What is the Spurling test? The Spurling test is a physical assessment to diagnose cervical radiculopathy or a pinched nerve in your neck. If you experience neck pain, a healthcare provider may offer this test.The Spurling test can tell your provider if something is squeezing or pressing against a nerve (nerve root compression) in your cervical spine.
Cervical radiculopathy is a clinical condition characterized by unilateral arm pain, numbness and tingling in a dermatomal distribution in the hand, and weakness in specific muscle groups associated with a single .During cervical spine trauma, complex intervertebral motions can cause a reduction in facet joint cartilage apposition area (CAA), leading to cervical facet dislocation (CFD). . The Effect of Axial Compression and Distraction on Cervical Facet Cartilage Apposition During Shear and Bending Motions Ann Biomed Eng. 2022 May;50(5):540-548. doi .The test is positive when the pain score (on a 0-10 visual analogue scale) is 3 points or higher during pressure on the middle third of the upper arm compared with two other areas. Axial traction — a combination of a positive Spurling test, axial traction test, and arm squeeze test increases the likelihood of cervical radiculopathy.
Each motion was superimposed with three axial conditions: (1) 50 N compression; (2) 300 N compression (simulating neck muscle contraction); and, (3) 2.5 mm distraction. Angular deflections, and principal and shear surface strains, of the bilateral C6 inferior facets were calculated from motion-capture data and rosette strain gauges, respectively.Spurling’s Test for Cervical Radicular Syndrome / Cervical Radiculopathy. Spurling’s test is a test with a low sensitivity of 50% and a good specificity of 83% to diagnose cervical radicular syndrome according to Wainner et al. (2003). Several authors have shown that this test has a rather low sensitivity and a high specificity.
of the spine have involved compression. Perhaps the earliest such study was Messerer's work on the me chanical properties of the vertebrae (2). He reported compression breaking loads ranging from 1.47-2.16kN for the lower cervical spine. Bauze and Ardran loaded humancadavericcervical spines in compressionand re-21
• Cervical Flexion Rotation Test • Cervical Compression, Jackson’s Compression, Maximum Foraminal . A more recent systematic review suggested that a combination of a positive Spurling’s test, axial traction (cervical distraction) test, and Arm Squeeze test may be used to increase the likelihood . roots, spinal nerves, and the .
The cervical spine is the most mobile region of the spine and enables the head with its sensory organs of sight, hearing and smell to be oriented independently from the trunk. . Coupled rotation patterns in cervical spine axial rotation can change when the head is kept level. Journal of Biomechanics. 2024:111924.
The C1 and C2 vertebrae are the first two vertebrae at the top of the cervical spine. Together they form the atlantoaxial joint, which is a pivot joint. The C1 sits atop and rotates around C2 below. More of the head’s rotational range of motion comes from C1-C2 than any other cervical joint. 1 Mead LB, Millhouse PW, Krystal J, Vaccaro AR. C1 . Flexion compression test. Procedure: The patient is seated. The examiner stands behind the patient and passively moves the cervical spine into flexion (tilts the patient’s head forward). Then axial compression is applied to the top of the head. Assessment: This is a good test of the integrity of the intervertebral disk. Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) of the spinal column occur secondary to an axial/compressive (and to a lesser extent, flexion) load with resultant biomechanical failure of the bone resulting in a fracture. VCFs by definition compromise the anterior column of the spine, thereby resulting in compromise to the anterior half of the vertebral body (VB) and the anterior .
Resultado da 30 Minutes of Slot Car Racing + Rental For Four People - Gather a group of friends or family members for an action-packed racing experience. Compete against each other and create lasting memories on the track. Fast Eddie's Slot Cars & Raceway offers an unforgettable experience that brings .
linear axial compression test on cervical spine|Cervical Orthopedic Tests